

Doctors measure levels of thyroid hormone in the blood if they suspect an overactive thyroid and measure levels of other hormones in people who may have pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma A pheochromocytoma is a tumor that usually originates from the adrenal glands’ chromaffin cells, causing overproduction of catecholamines, powerful hormones that induce high blood pressure and. This blockage causes unstable angina or a heart attack (myocardial infarction), depending on the location and amount. Doctors may measure other substances in the blood (cardiac markers) if the person has other symptoms that suggest a possible acute coronary syndrome Acute Coronary Syndromes (Heart Attack Myocardial Infarction Unstable Angina) Acute coronary syndromes result from a sudden blockage in a coronary artery. Doctors do a complete blood count and measure serum electrolytes, including potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Some commercially available products such as fitness trackers, which monitor heart rate, and other trackers that monitor track heart rhythms, are available for smart phones and watches but provide more limited information. Doctors can then use an external monitor to check the loop recorder for abnormal heart rhythms. This device is called a loop recorder, and it continuously monitors the person's heartbeat.
FEEL WIRD FLUTTER IN CHEST SKIN
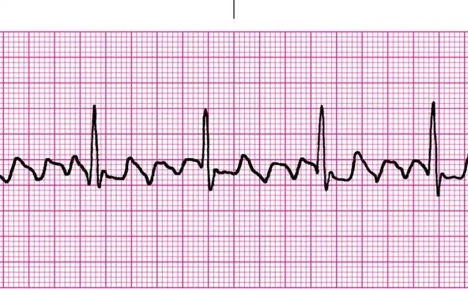
In some people, doctors may insert a device underneath the skin to monitor the heart beat. Thus, people who have intermittent palpitations may need to wear an ECG monitor for a day or two (Holter monitoring-see figure ) or for a longer period (event recorder) to detect brief or irregularly occurring abnormal rhythms. However, only a few of the possible causes produce an abnormal ECG when people are not having palpitations. If the ECG is done while the person is having palpitations or an abnormal pulse rate, the diagnosis is usually clear. This record, the electrocardiogram (also known as an ECG). read more ) can develop chest pain due to angina or a heart attack (which may be fatal).ĮCG Electrocardiography Electrocardiography (ECG) is a quick, simple, painless procedure in which the heart’s electrical impulses are amplified and recorded. The heart muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen-rich blood.

People who have narrowing of the arteries to the heart muscle ( coronary artery disease Overview of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Coronary artery disease is a condition in which the blood supply to the heart muscle is partially or completely blocked. A rapid heart rate also increases the oxygen needs of the heart muscle. Heart failure occurs mainly in people who have previously had heart failure or a heart attack, although it can occur in other people if the heart rate is very fast or if the heart beats too fast for a long time. If the heart goes too fast, it may not be able to pump blood adequately, and people may feel faint or pass out or develop heart failure Heart Failure (HF) Heart failure is a disorder in which the heart is unable to keep up with the demands of the body, leading to reduced blood flow, back-up (congestion) of blood in the veins and lungs, and/or. read more ).Īrrhythmias that cause the heart to beat too fast can cause complications (particularly in older people). People may have episodes of a very rapid heartbeat. read more ), disorders of heart valves, and conduction system disturbances (for example, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a disorder in which an extra electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles is present at birth. read more (acute coronary syndrome), congenital heart diseases (for example, the Brugada syndrome or congenital long QT syndrome Torsades de Pointes Ventricular Tachycardia Torsades de pointes ventricular tachycardia is a specific type of ventricular tachycardia that occurs in people who have a particular disorder of the heart's electrical activity called a long. read more, heart attack Acute Coronary Syndromes (Heart Attack Myocardial Infarction Unstable Angina) Acute coronary syndromes result from a sudden blockage in a coronary artery. A person with angina usually has discomfort or pressure beneath the. Serious heart disorders include angina Angina Angina is temporary chest pain or a sensation of pressure that occurs while the heart muscle is not receiving enough oxygen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
